Einsatzmöglichkeiten von Talsim-NG: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Doeser (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
(Diese Seite wurde zum Übersetzen freigegeben) |
||
| (47 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 2 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
<languages/> | <languages/> | ||
<translate> | <translate> | ||
<!--T:3--> | |||
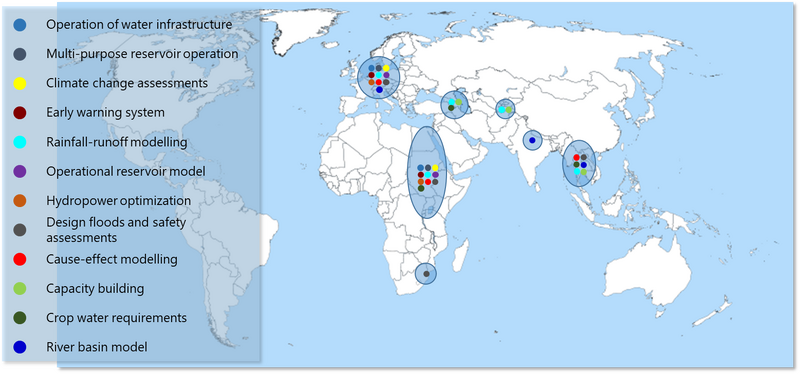
[[Datei:TalsimNG_Applications.png|800px|center]] | |||
<!--T:1--> | <!--T:1--> | ||
Talsim-NG stellt für viele verschiedene Aufgabenstellungen das passende Werkzeug dar: | Talsim-NG stellt für viele verschiedene Aufgabenstellungen das passende Werkzeug dar: | ||
| Zeile 10: | Zeile 14: | ||
* Dimensionierung wasserwirtschaftlicher Anlagen | * Dimensionierung wasserwirtschaftlicher Anlagen | ||
* [[Operationeller Einsatz von Talsim-NG]] für den wasserwirtschaftlichen Betrieb in Verbindung mit einem Monitoringsystem | * [[Operationeller Einsatz von Talsim-NG]] für den wasserwirtschaftlichen Betrieb in Verbindung mit einem Monitoringsystem | ||
<!--T:2--> | <!--T:2--> | ||
| Zeile 18: | Zeile 23: | ||
* Beliebige Anforderung und Ausgabe von Zustandsgrößen | * Beliebige Anforderung und Ausgabe von Zustandsgrößen | ||
* Berechnung aussagekräftiger Kenngrößen (Bilanzen oder Sicherheiten) | * Berechnung aussagekräftiger Kenngrößen (Bilanzen oder Sicherheiten) | ||
====Process-based hydrological modelling==== <!--T:6--> | |||
<!--T:4--> | |||
Processes and features: | |||
* Precipitation-runoff component + snow compaction | |||
* Soil moisture and crop water requirements calculation | |||
* Up to 6 soil layers | |||
* Snow simulation | |||
* Hybrid hydrological/hydraulic flood routing | |||
* Non-linear atmosphere-vegetation-soil interface | |||
* Hybrid hydrological/hydraulic flood routing, | |||
* Hydraulic modelling of weirs, diversions, pipes | |||
* Crop water requirements | |||
* Irrigation | |||
* Reservoir operation | |||
* Water quality | |||
* Hydropower | |||
* Conceptual groundwater modelling | |||
* Nested modelling of sub-basins with high spatial resolution | |||
* Generic rule builder for water management options | |||
* Pre-processing and post-processing | |||
* Multicriteria optimization | |||
* Time series manager | |||
* Project and scenario manager | |||
* Client-Server architecture | |||
<!--T:5--> | |||
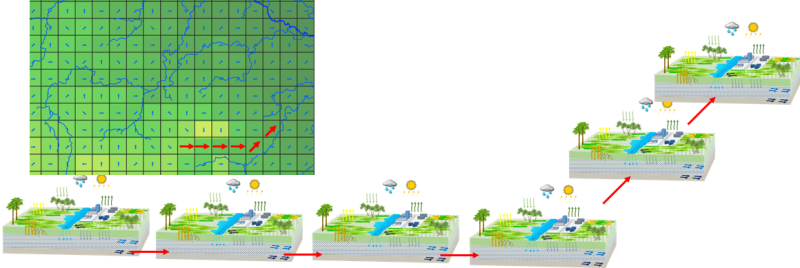
====Gridded or watershed oriented approach==== | |||
Talsim-NG can be used for both gridded or watershed oriented concepts | |||
<gallery mode="packed" heights=300px> | |||
File:Gridded model approach.png|gridded | |||
File:Hru.png|watersheds | |||
</gallery> | |||
<!--T:7--> | |||
====Atmosphere / Vegetation / Soil Interface for Crop Water Requirements and Irrigation==== | |||
[[Einzugsgebiet]] | |||
<!--T:8--> | |||
====Linkage of flow components==== | |||
[[Datei:Linkage of flow components.png|800px|center]] | |||
Surface and sub-surface flow components between elements are interconnected. If soil downstream is saturated, flow from the upstream cell is impeded: | |||
* Backwater effects | |||
* Surface flow accumulates from element to element | |||
<!--T:9--> | |||
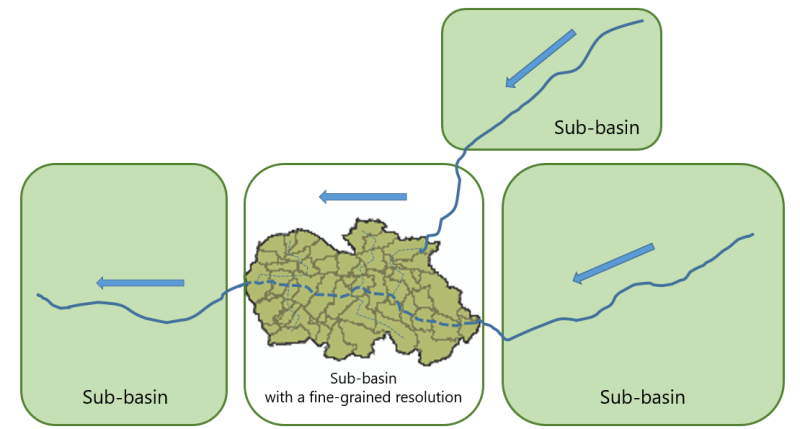
====Nested modelling==== | |||
A model within a model! | |||
<!--T:10--> | |||
If necessary, sub-basins can be simulated with different resolutions and levels of detail within a large river basin model. | |||
[[Datei:Nested modelling.png|800px|center]] | |||
<!--T:11--> | |||
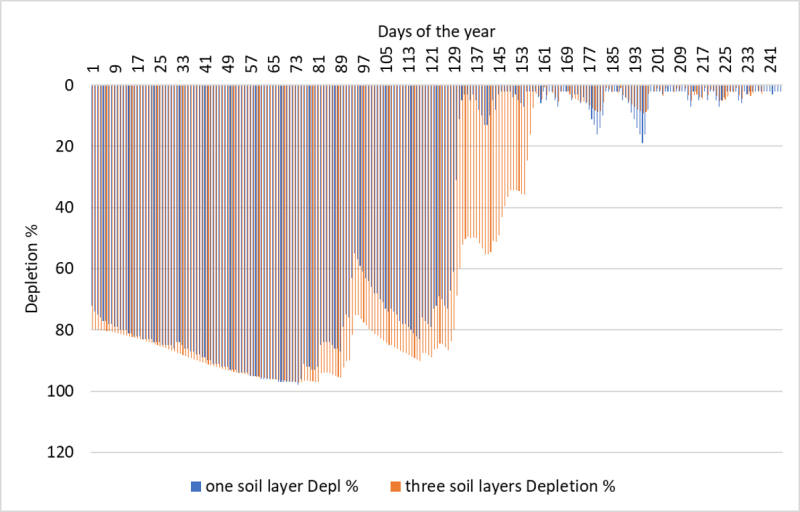
====Crop water requirements==== | |||
Comparison CropWat (FAO) vs. Talsim-NG | |||
[[Datei:Crop water requirements.png|800px|center]] | |||
<!--T:12--> | |||
====Hybrid hydrological / hydraulic modelling==== | |||
[[Datei:Hybrid hydrological and hydraulic modelling.png|800px|center]] | |||
<!--T:13--> | |||
====Water quality and stratification modelling==== | |||
[[Datei:Water quality and stratification modelling.png|800px|center]] | |||
<!--T:14--> | |||
====Talsim-NG in operational mode==== | |||
Automation from data retrieval to sending e-mails when operational simulation runs are required | |||
[[Datei:Talsim-NG in operational mode.png|800px|center]] | |||
<!--T:15--> | |||
====Client-Server environment==== | |||
[[Datei:Client-Server environment.png|800px|center]] | |||
<!--T:16--> | |||
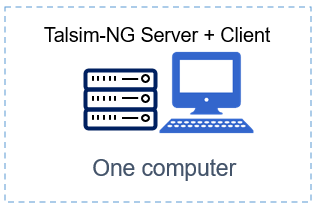
====Emulated Client-Server environment==== | |||
Emulated client-server environment | |||
Client and Server run on the same computer | |||
[[Datei:Emulated Client-Server environment.png|800px|center]] | |||
<!--T:17--> | |||
====Participatory modelling / serious gaming==== | |||
Talsim-NG as tool for capacity building:<br> | |||
<!--T:18--> | |||
1) Topic: Live interaction between water managers<br> | |||
2) Tool: Put operators in various positions | |||
* upstream perspective, downstream perspective | |||
* exposes stakeholders to different levels of dependencies | |||
* shows effects with/without data sharing | |||
* demonstrates effects with/without cooperation | |||
* mimics flood / drought events | |||
3) Activity: A group of water managers plays at the same time | |||
</translate> | </translate> | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 26. Januar 2024, 12:22 Uhr
Talsim-NG stellt für viele verschiedene Aufgabenstellungen das passende Werkzeug dar:
- Niederschlag-Abfluss-Simulation (sowohl Hochwasser als auch Langzeitszenarien)
- Flussgebietsmodellierung und -bewirtschaftung
- Bewirtschaftung von Speichern, Hochwasserrückhaltebecken, Talsperren bzw. Talsperrensystemen für verschiedene Nutzungen (Wasserversorgung, Hochwasserschutz, Niedrigwasseraufhöhung, Energiegewinnung, Einhaltung von Mindestabgaben, Freizeitnutzung)
- Wassergüteberechnung
- Kopplung von Wassermengen- und Wassergütebetrachtung
- Dimensionierung wasserwirtschaftlicher Anlagen
- Operationeller Einsatz von Talsim-NG für den wasserwirtschaftlichen Betrieb in Verbindung mit einem Monitoringsystem
Ebenso stellt Talsim-NG für viele wasserwirtschaftliche Untersuchungen die passenden Funktionalitäten bereit:
- Interne Zeitreihenverwaltung
- Verwaltung der Simulationen inklusive der Ergebnisse zur Gegenüberstellung
- Langzeitsimulation / Kurzfristprognosen
- Beliebige Anforderung und Ausgabe von Zustandsgrößen
- Berechnung aussagekräftiger Kenngrößen (Bilanzen oder Sicherheiten)
Process-based hydrological modelling
Processes and features:
- Precipitation-runoff component + snow compaction
- Soil moisture and crop water requirements calculation
- Up to 6 soil layers
- Snow simulation
- Hybrid hydrological/hydraulic flood routing
- Non-linear atmosphere-vegetation-soil interface
- Hybrid hydrological/hydraulic flood routing,
- Hydraulic modelling of weirs, diversions, pipes
- Crop water requirements
- Irrigation
- Reservoir operation
- Water quality
- Hydropower
- Conceptual groundwater modelling
- Nested modelling of sub-basins with high spatial resolution
- Generic rule builder for water management options
- Pre-processing and post-processing
- Multicriteria optimization
- Time series manager
- Project and scenario manager
- Client-Server architecture
Gridded or watershed oriented approach
Talsim-NG can be used for both gridded or watershed oriented concepts
Atmosphere / Vegetation / Soil Interface for Crop Water Requirements and Irrigation
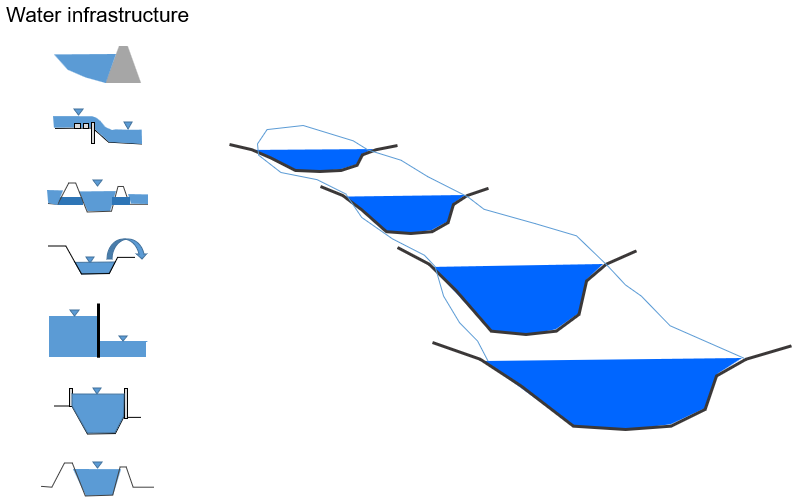
Linkage of flow components
Surface and sub-surface flow components between elements are interconnected. If soil downstream is saturated, flow from the upstream cell is impeded:
- Backwater effects
- Surface flow accumulates from element to element
Nested modelling
A model within a model!
If necessary, sub-basins can be simulated with different resolutions and levels of detail within a large river basin model.
Crop water requirements
Comparison CropWat (FAO) vs. Talsim-NG
Hybrid hydrological / hydraulic modelling
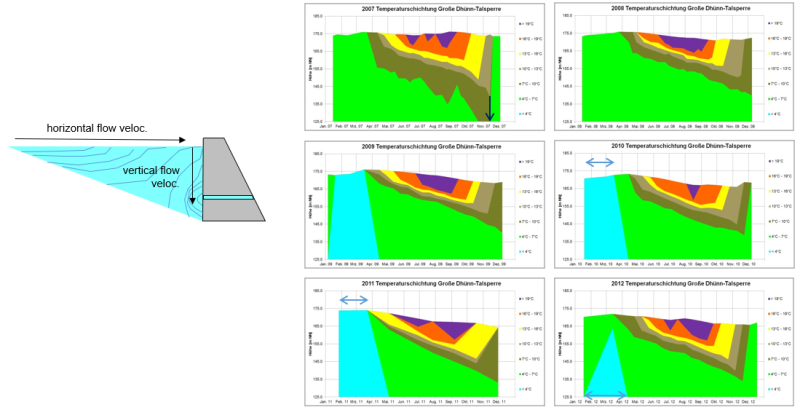
Water quality and stratification modelling
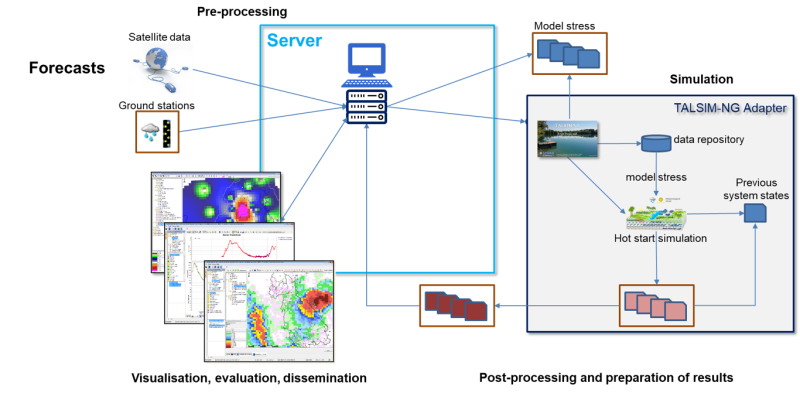
Talsim-NG in operational mode
Automation from data retrieval to sending e-mails when operational simulation runs are required
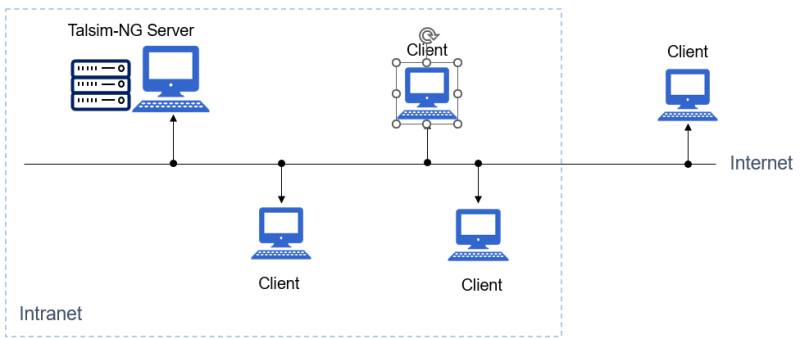
Client-Server environment
Emulated Client-Server environment
Emulated client-server environment Client and Server run on the same computer
Participatory modelling / serious gaming
Talsim-NG as tool for capacity building:
1) Topic: Live interaction between water managers
2) Tool: Put operators in various positions
- upstream perspective, downstream perspective
- exposes stakeholders to different levels of dependencies
- shows effects with/without data sharing
- demonstrates effects with/without cooperation
- mimics flood / drought events
3) Activity: A group of water managers plays at the same time